
 G-proteins
Transcription and
signalling
G-proteins
Transcription and
signalling 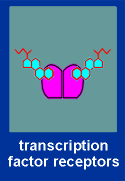
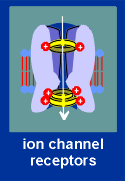
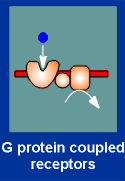
| There are four major mechanisms in cell signaling, based on the nature of the receptor molecule receiving the signal. The receptor molecule can be |
-
(1) an ion channel,
-
(2) a membrane-bound tyrosine kinase,
-
(3) a G-protein-coupled receptor, or
-
(4) a transcription factor.